What is Face Recognition?
We humans have been able to perform face recognition seamlessly in our daily lives. With the advancements in technology particularly high-powered cameras in smartphones and active use of visual data on buzzing social media platforms, so much of image data has given rise to a demand to analyse it. The applications of this analysis vary from security, surveillance, smart cards, media content compliance to law enforcement. We can understand face recognition as capturing the facial data, analysing it to compare with the already present database to identify the person. Did you know?
Takeo Kanade developed the first face recognition system in 1973.
Why Use Face for Recognition?
Biometric techniques have emerged as a more promising solution to identifying persons of interest. These techniques include fingerprint, iris and retina, and voice besides face recognition. There are certain drawbacks associated with them which might render it useless, such as in case of damaged epidermis, body motion, background voice and auditory fluctuations. Not to forget that they work under scenarios of cooperative users only. Face recognition is an exception to these downsides, owing to its nature of action - natural and non-intrusive. Based on user cooperation, use cases of face recognition are broadly classified as:
- Cooperative user scenario Examples include government ID verification, KYC verification, and other scenarios where the user will let the camera take visual data in the proper manner.
- Non cooperative user scenario Examples include surveillance, mug-shot, post event analysis, forensics and so on where the user is unaware of data being captured or deliberately trying to deliver improper visual data.
Image Recognition Process
Given a visual input, the first step is to segment the face from the background. Next step is localisation of facial landmarks like the eyes, nose, mouth etc followed by normalisation of the face to suit the face recognition algorithms depending on pose and illumination of the face in the visual input. This normalised data is used to extract features to learn the differences in the different data visuals. These features are then used to find a match from the database.

Face Recognition Process-flow.
General Difficulties
Face recognition encounters many challenges as not only are the faces of every individual unique but also that there are no particular set of attributes that can distinguish one face from another. A change in factors such as illumination, angle of view, image resolution, gender, facial hair, expression, affect facial appearances. We can classify these factors as:
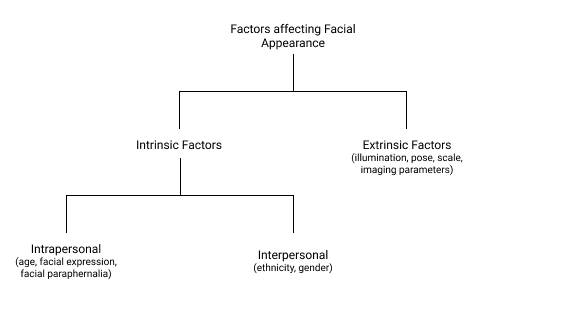
Factors affecting facial appearance.
Other challenges include complex nonlinear manifold nature of face and enormous difference in the ratio of high dimensionality data to the sample size.
Conclusion
However, over the past few decades we have been able to develop many new techniques to overcome these drawbacks.